OpenAI has officially launched Realtime API and gpt-realtime, its most advanced speech-to-speech model, moving the Realtime API out of beta with a suite of enterprise-focused features. While the announcement marks real progress in voice AI technology, a closer examination reveals both meaningful improvements and persistent challenges that temper any revolutionary claims.
Technical Architecture and Performance Gains
GPT-Realtime represents a fundamental shift from traditional voice processing pipelines. Instead of chaining separate speech-to-text, language processing, and text-to-speech models, it processes audio directly through a single unified system. This architectural change reduces latency while preserving speech nuances that typically get lost in conversion processes.
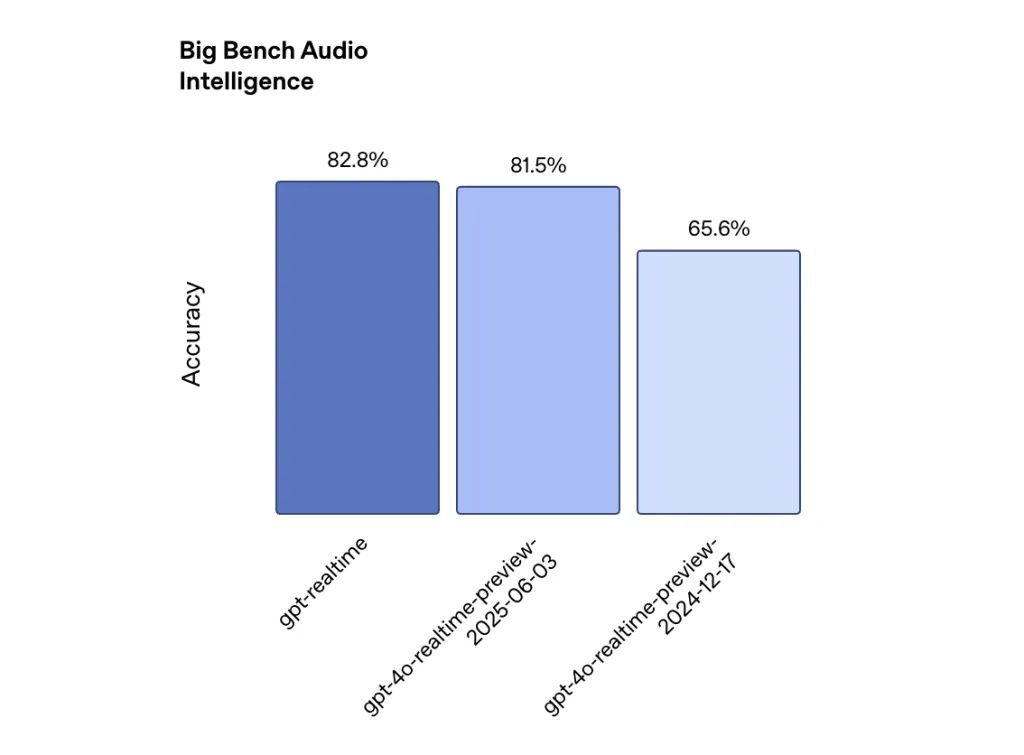
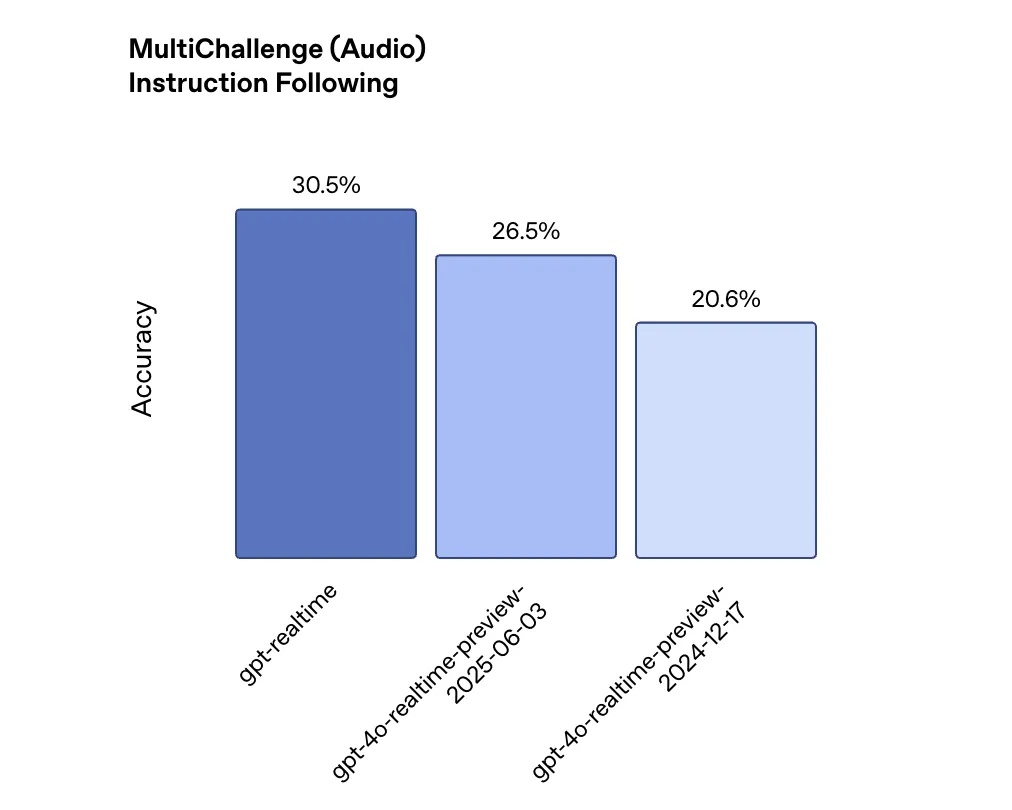
The performance improvements are measurable but incremental. On the Big Bench Audio evaluation measuring reasoning capabilities, GPT-Realtime scores 82.8% accuracy compared to 65.6% from OpenAI’s December 2024 model—a 26% improvement. For instruction following, the MultiChallenge audio benchmark shows GPT-Realtime achieving 30.5% accuracy versus the previous model’s 20.6%. Function calling performance improved to 66.5% on ComplexFuncBench from 49.7%.
These gains are significant but highlight how far voice AI still has to go. Even the improved instruction following score of 30.5% suggests that seven out of ten complex instructions may not be properly executed.

Enterprise-Grade Features
OpenAI has clearly prioritized production deployment with several new capabilities. The API now supports Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) integration, allowing voice agents to connect directly to phone networks and PBX systems. This bridges the gap between digital AI and traditional telephony infrastructure.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) server support enables developers to connect external tools and services without manual integration. Image input functionality allows the model to ground conversations in visual context, enabling users to ask questions about screenshots or photos they share.
Perhaps most importantly for enterprise adoption, OpenAI has introduced asynchronous function calling. Long-running operations no longer disrupt conversation flow—the model can continue speaking while waiting for database queries or API calls to complete. This addresses a critical limitation that made previous versions unsuitable for complex business applications.
Market Positioning and Competitive Landscape
The pricing strategy reveals OpenAI’s aggressive push for market share. At $32 per million audio input tokens and $64 per million audio output tokens—a 20% reduction from the previous model—GPT-Realtime is positioned competitively against emerging alternatives. This pricing pressure suggests intense competition in the speech AI market, with Google’s Gemini Live API reportedly offering lower costs for similar functionality.notablecap+2
Industry adoption metrics indicate strong enterprise interest. According to recent data, 72% of enterprises globally now use OpenAI products in some capacity, with over 92% of Fortune 500 companies estimated to use OpenAI APIs by mid-2025. However, voice AI specialists argue that direct API integration isn’t sufficient for most enterprise deployments.
Persistent Technical Challenges
Despite the improvements, fundamental speech AI challenges remain. Background noise, accent variations, and domain-specific terminology continue to impact accuracy. The model still struggles with contextual understanding over extended conversations, a limitation that affects practical deployment scenarios.
Real-world testing by independent evaluators shows that even advanced speech recognition systems face significant accuracy degradation in noisy environments or with diverse accents. While GPT-Realtime’s direct audio processing may preserve more speech nuances, it doesn’t eliminate these underlying challenges.
Latency, while improved, remains a concern for real-time applications. Developers report that achieving sub-500ms response times becomes difficult when agents need to perform complex logic or interface with external systems. The asynchronous function calling feature addresses some scenarios but doesn’t eliminate the fundamental tradeoff between intelligence and speed.
Summary
OpenAI’s Realtime API marks a tangible, if incremental, step forward in speech AI, introducing a unified architecture and enterprise features that help overcome real-world deployment barriers, combined with competitive pricing that signals a maturing market. While the model’s improved benchmarks and pragmatic additions—such as SIP telephony integration and asynchronous function calling—are likely to accelerate adoption in customer service, education, and personal assistance, persistent challenges around accuracy, context understanding, and robustness in imperfect conditions make it clear that truly natural, production-ready voice AI remains a work in progress.
Check out the Technical details here. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.


